The first international teacher training course for skills development began on Saturday evening, November 16,
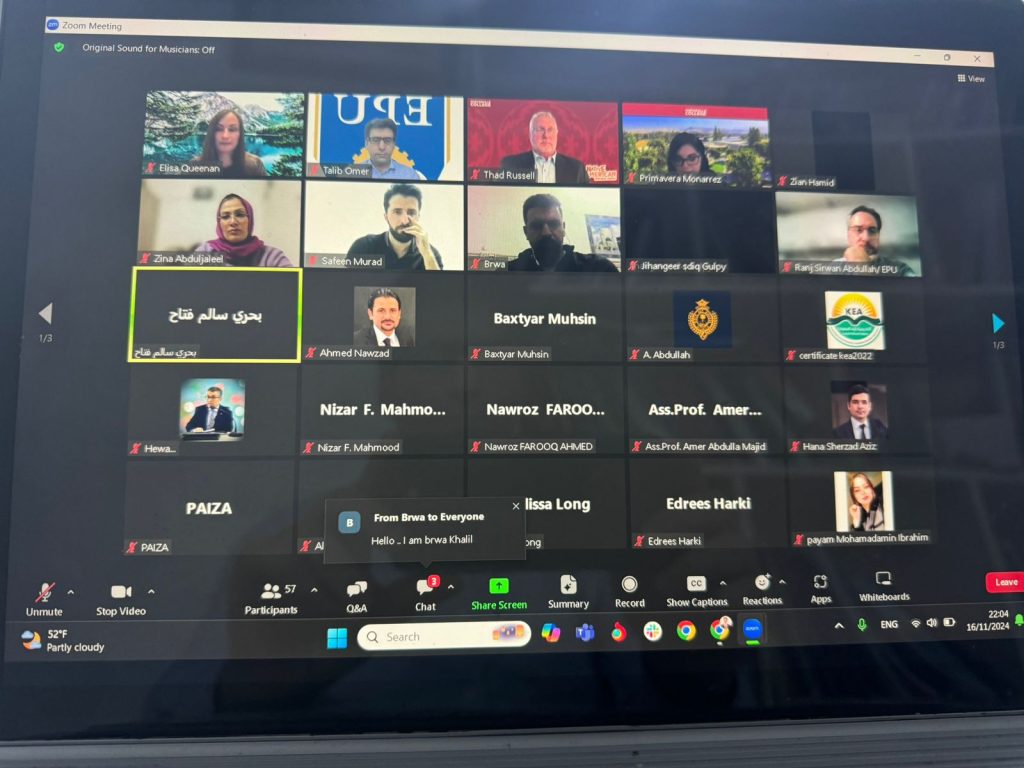
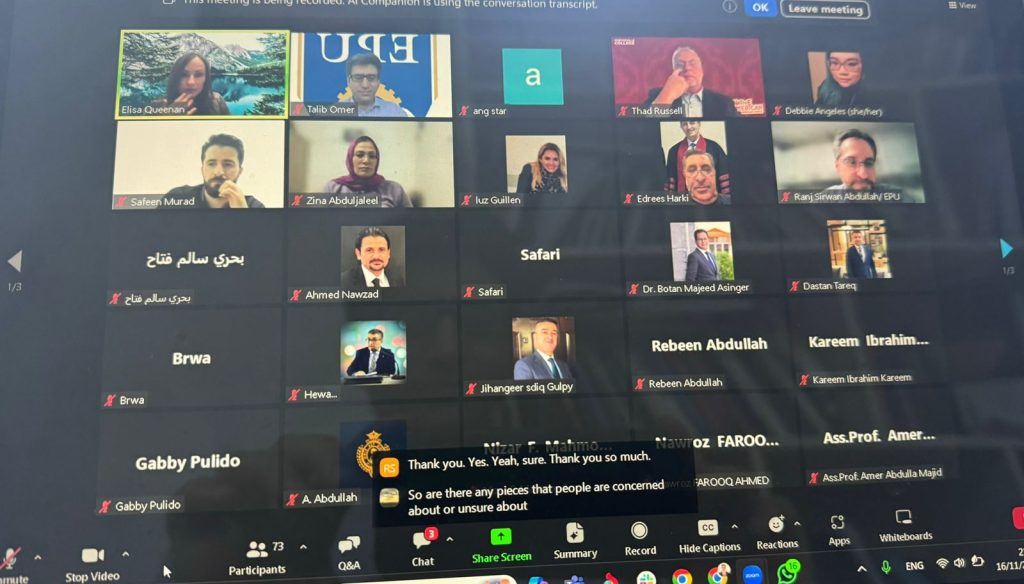
The first international teacher training course for capacity development was attended by Prof. Dr Idris Mohammed Tahir Harki, Rector of Erbil Polytechnic University; Dr. Botan Majid, Vice Rector for Scientific Affairs and Higher Education; Dr Talib Omer, Dean of Mergasor Technical Institute and Dr Ranj Sirwan, Director General of the University’s Scientific Research Center.
Training is aimed at further developing and enriching practical lessons in the field of education , and it is an opportunity for everyone to use their abilities to learn sciences.
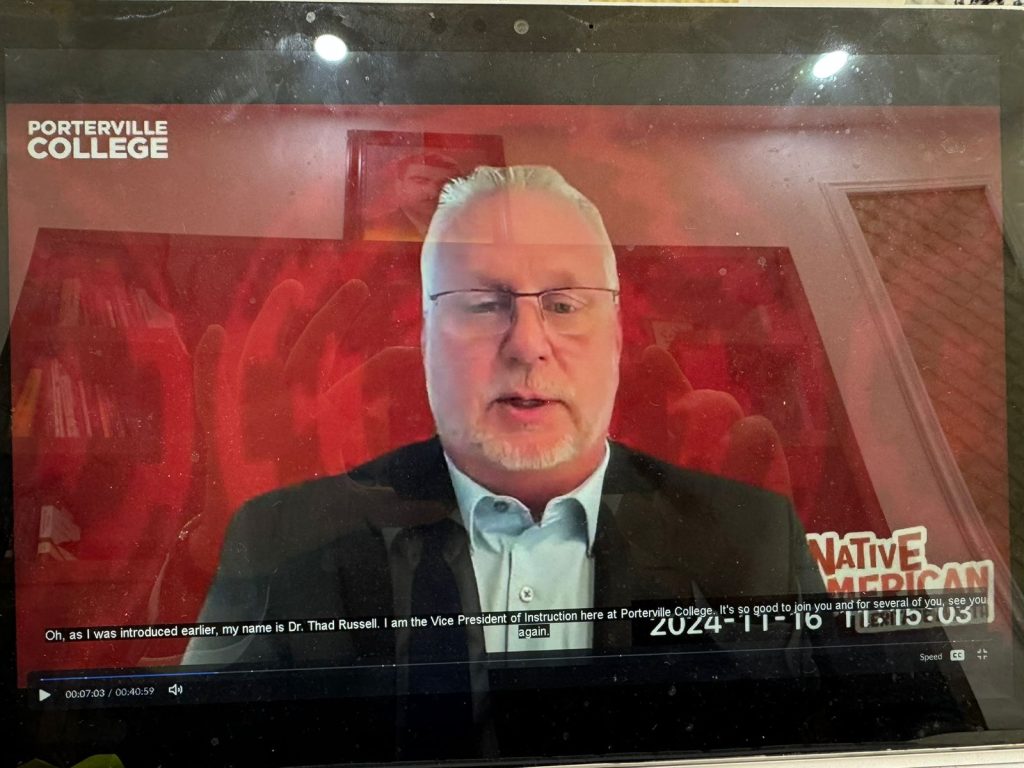
The Training course was begun by addressing key note speakers’ speech including president Dr Primavera Monnarrez and Chancellor Dr Steven Bloomberg, and Vice -President Dr Thad Russel for more than 50 university teachers and more than 20 teachers, directors and supervisors of education of Soran Independent Administration, which will continue for three months under the supervision of teachers of Portville College in a professional manner.
The aims of the training is to create platforms and networks for educators to share best practices, resources, and research findings internationally.
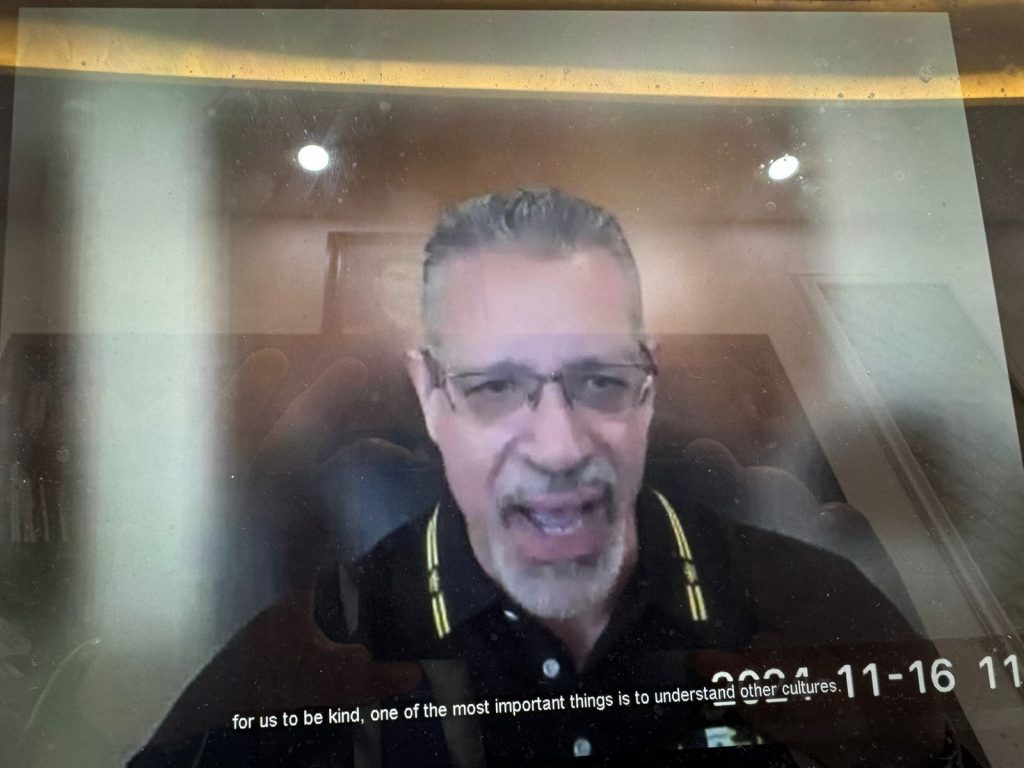
Also to foster Cultural Empath and awareness among educators to promote a global perspective in education.
International collaboration brings us together from different cultural, educational, and professional backgrounds. This diversity fosters the exchange of innovative teaching methods, strategies, and perspectives that can broaden our approaches to pedagogy/andragogy.
Building connections with educators worldwide expands professional networks significantly. These networks can lead to collaborative campus projects and institutional partnerships. Collaborative efforts enhance the quality of teaching and student collaborative projects and contribute to the global advancement of knowledge in various academic fields.
Mergasor Technical Institute and Porterville College in California have become sister colleges for enhancing international academic collaboration.
Mergasor Technical Institute has always tried to work to educate and serve all aspects of society through its academic relations.